Gartner defines a Metaverse as a collective virtual shared space created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical and digital reality. It is persistent, providing enhanced immersive experiences, as well as device-independent, and accessible through any type of device, from tablets to head-mounted displays. It also predicts that by 2026, 25% of people will spend at least one hour per day on the Metaverse.
While the majority around the globe are still coming to terms with Metaverse and all that it encapsulates, early investments by pioneers like Meta (the company), Fortnite (the game), Somnium Space (a VR world builder), IMVU (an avatar-based 3D social network) and many others have swollen the Metaverse market size to about $47bn (with around $10bn out of this committed by Meta itself) with predicted market size of around $800bn by 2024. We are talking of a 16 times growth rate within the next 2-3 years, which is mind-numbingly mammoth.
Building blocks of metaverse- What comprises this evolving magical world?
Key building blocks of metaverse:
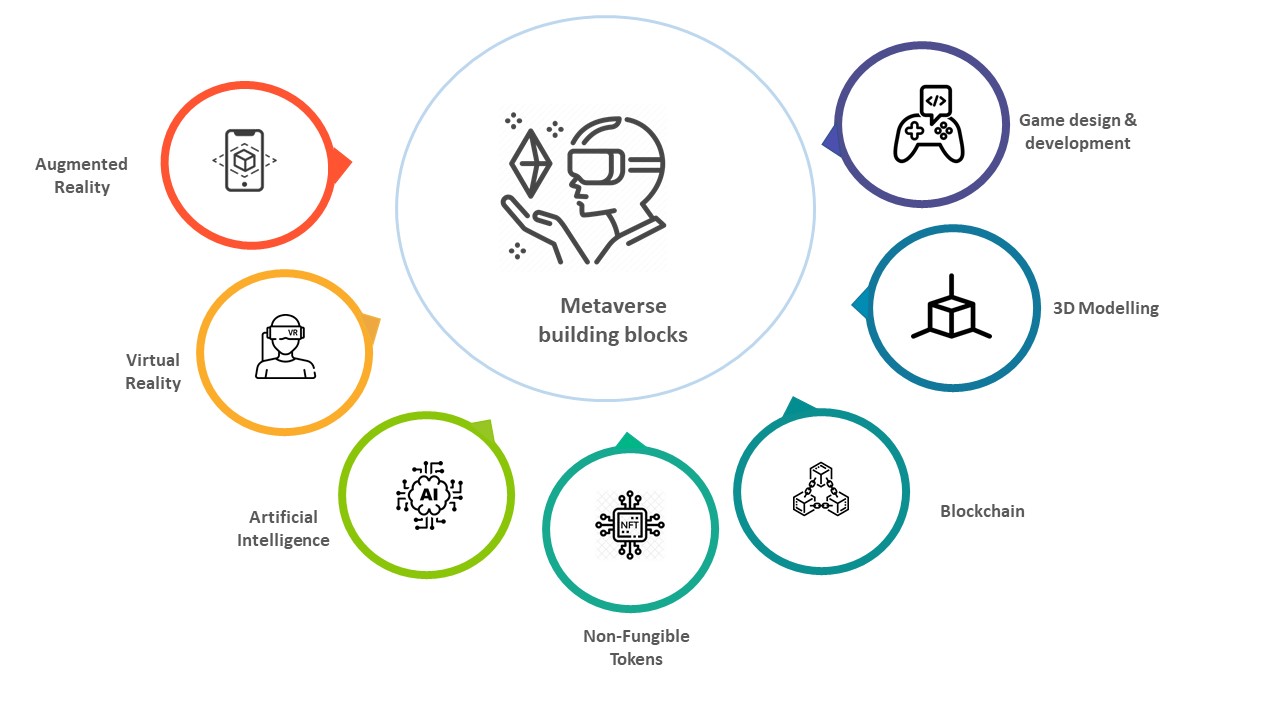
Let’s evaluate each of the building blocks:
- Augmented reality (AR): Pokémon Go showed us the beauty of augmented reality some years back. Thereafter, many popular brands like Ikea showed us how augmented reality can help people visualize product placements in their living rooms even before they purchase them. In the Metaverse, AR will play an active part in differentiating brands, low-cost visualization of costly assets, enabling virtual try-on (of make-up, shoes, jewelry, etc.), for immersive gamified experience, enriched quality assurance, etc. The AR market, in keeping with the larger Metaverse phenomenon, is expanding at a rapid rate and is poised to touch $88.4bn by 2026 from $14.7bn in 2020.
- Virtual reality (VR): Virtual reality is the use of computer technology for creating a simulated environment. An immersive and interactive virtual reality allows the audience to interact with the experience, turning them into active participants. In a virtual setup, the participant can turn around, jump up, bend down, look up, move around, and do anything that he/she would in the real world. Use cases of virtual reality applications saw a quantum growth during the pandemic with virtual conferences, virtual games, virtual exhibitions, virtual events, virtual training, virtual computer vision, and interactive virtual tours seeing widespread traction. The global virtual reality headsets market size is projected to reach USD19. 8 Billion by 2026, from USD 6.8 Billion in 2020, at a CAGR of 19.5%.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a key ingredient in digitalization across industries- be it retail, manufacturing, healthcare, or any other. Whether machine learning, deep learning, business intelligence, natural language processing (NLP), or AI-powered chatbots, enterprises are better served with insights and analytics, courtesy of AI. In the Metaverse, AI plays a role in every step of the way. From AIOps at an infrastructural plane, enabling blockchain-driven smart contracts to power data-driven immersive experiences across various digital interfaces, to hyper-personalizing experiences at the top, AI is a vital cog in the wheel of the Metaverse. The global artificial intelligence market size was valued at USD 51.08 Billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 641.30 Billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 36.1%.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFT): NFTs are tokens used to represent ownership of unique items. Several celebrities like Reese Witherspoon, Eva Longoria, Serena Williams, etc. have used NFT profile pictures on Twitter. NFTs allow creators to tokenize things like art, collectibles, even real estate. “Non-fungible” means it’s unique and can’t be replaced with something else. For example, the currency is fungible — can exchange one $100 note for another. But NFTs are one of a kind and can be bought by users directly from the creators. Hence, it has the special aura of something prized and unique. For every such NFT sold, creators can earn without depending on any intermediary. The global non-fungible token (NFT) market size reached USD 340.0 Million in 2020 and is expected to register a rapid revenue CAGR in the forthcoming years.
- Blockchain services: It wouldn’t be inappropriate to say that blockchain would be a popular trading medium on the Metaverse; while Metaverses will most certainly allow for buying and selling using real currencies too, blockchain would make the experience much more disintermediated, seamless, and secure. Blockchain will also form the basis of Decentralized Apps (DApps) and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO). The blockchain market size is projected to grow from USD 4.9 billion in 2021 to USD 67.4 billion by 2026.
- 3D modeling: 3D modeling refers to the development process of mathematical representation of a particular surface of any object in 3 dimensions by using advanced-level software. With avatars set to represent each human entity on the Metaverse, and virtual exhibitions, virtual events, and shows becoming prominent uses cases in the Metaverse, the demand for 3D artists is growing like never before across industries, such as animation, film, gaming, architecture, and interior designing. The 3D mapping and modeling market size was valued at USD 3.64 Billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 13.15 Billion by 2028.
- Game design, development, and commercialization: With more than 2.7 billion gamers around the world and around 48% of gaming companies working on AR/VR games, the estimated size of the gaming industry is in the range of $200bn globally and is poised to reach $545.88 by 2028 with a CAGR of 13.2%.
Gaming companies like Roblox and Epic Games are leading the way in building metaverses by building virtual worlds, where millions of gamers interact, play, and take part in an experiential economy. Some pro gamers even make a living inside these Metaverses by selling their digital collectibles. Some companies like Roblox also held their holiday parties in the Metaverse while companies like Fortnite treated their fans to a Travis Scott concert.
Metaverse Brings Together The Experience Economy
The biggest property of Metaverse is bringing together various dimensions of the “Experience Economy”. Experience is a function of the right infrastructure with intelligent interfaces that supports the decentralized existence of data closer to devices while enabling the consumption of immersive experiences, thus encouraging the creator community to compose and publish innovative pieces of work in the form of NFTs, which when discovered through multifaceted marketing results in esoteric experiences which is unprecedented. Such experiences, in turn, produce massive units of data that get fed back into the loop to create a continuum of the experience economy. The below illustration explains this loop.
Metaverse As A Service (MaaS) Is Taking Off Already
This whole decentralized, permission-less, semantic web-oriented, AR/VR/XR/MR/AI-driven, hyper-connected, and ubiquitous nature of the Metaverse opens it to a myriad of business uses across industries. The sheer potential of this now nascent industry is forcing many technology leaders like Meta, Google, BMW, Nissan, and many others to not only invest in this but also compel many IT companies to package this as a service where they can actually go ahead and create metaverses for their clients. The industry is expected to grow 16 times in the next 3-4 years and, as always, early movers would get the cream of the cake. But what would a metaverse service catalog look like? While we evaluated the building blocks earlier in this piece, each such building block will have a myriad of services under it. Each such service area is vast in nature and possibly the subsequent blogs will look to deep dive into a prominent few services. But the fact remains that this ever-growing catalog of Metaverse possibilities needs to be packaged “as a service” and offered to the market at the earliest, as the sheer revenue potential cannot be overlooked. Let’s take a look at a sample metaverse catalog with a scope of many more services that can get added in the coming years.
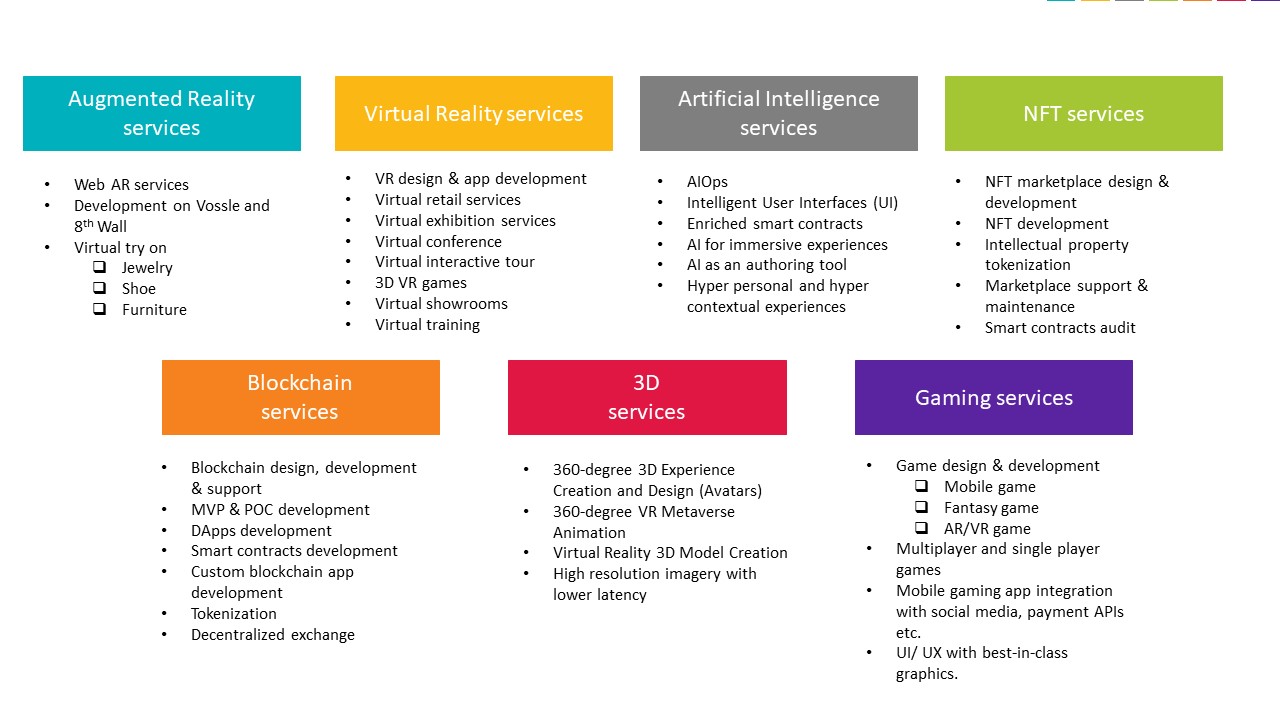
Figure: The evolving Metaverse service catalog
Security On Metaverse Will Be Key To Its Growth
Metaverse is still at its genesis phase and already concerns are being raised about potential security loopholes that could drain away its usefulness. One concern being raised is that of “Avatar Impersonation”- a kind of potential identity theft of Metaverse, where an unwanted element can hack into the Metaverse and manipulate the avatars for shady gains. To combat this, experts are mulling building biometrics into the hardware so that the VR headset can recognize and record the iris of the person and associate it with his/her avatar to prevent such social engineering.
Invisible avatar eavesdropping is another potential security breach that’s coming to the fore where disruptive elements may invisibly join meetings and listen to the conversations. Likewise, most recently Facebook identified a few users complaining of sexual harassment on the Metaverse and hence brought about the “personal boundary” tool to make users feel like they have nearly four feet between their virtual avatar and others when they access the immersive Horizon Worlds and Horizon Venues apps through VR headsets.
As the metaverse ecosystem expands, it is equally important for cyber security experts to conceptualize potential security threats and create mitigation measures for each to make the metaverse as safe and secure as possible.
Conclusion
The world started talking about the Metaverse in the summer of 2021 when Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg started off his plan to focus his company on building what he imagined would be the future of society, business, leisure, and culture: the metaverse. He, later on, changed the name of his company from Facebook to Meta. Since then, this space has stayed abuzz with activities with several big technology players investing, ideating, and exploring the future of the 3D virtual world in this “parallel” verse. Many have started visualizing “Metaverse as a Service” as a service offering by bringing together the myriad building blocks of AR, VR, AI, blockchain, NFTs, 3D, and gaming together. This is a fast-growing space, and it is imperative that the IT industry watches this space closely, stitches in the right partnerships, conducts a few rapid POCs and MVPs, and then rolls out a full-fledged Metaverse as a Service (MaaS) proposition. It may not be long before requests for responses are solicited as NFTs and due diligence is conducted through virtual networks. The promise is immense, and it will be important for all the stakeholders to come together to identify valuable use cases and leverage the opportunities in Metaverse to its complete might while ensuring the security is held tight at all times.












